We have an insatiable demand for technology in all aspects of our lives. We need technology to make our work more efficient, our lives safer and healthier, and our lifestyles more comfortable. Central to the technology are the semiconductor chips that are responsible for the computations that make our electronics smarter. Experts have been warning us for some time of the chip shortage due to the demand growth that is outpacing supply capacity.
The global semiconductor chip crisis shows no signs of ending soon.
Such a major shortfall can have more far-reaching consequences than you might think. Companies are now anticipating reducing their manufacturing capacity at various times because the chips that run their products are not available. Repair and maintenance of existing systems are being postponed. The shortage crisis could lead to factory shutdowns, jobs lost, longer wait times, and higher prices. It can leave critical infrastructure unmended, even impacting our safety and wellbeing.
What’s Causing the Chip Shortage?
There are many reasons for the chip shortage crisis.
First, there are only a limited number of companies around the world that have the ability to manufacture high-end chips. They include TSMC, Intel, and Global Foundries, just to name a few. Production line upgrades cost billions of dollars and it is difficult to keep up with the advancements of the new manufacturing techniques for nanoscale-sized transistors.
Second, electronic products are getting smarter, and that means more processing. For example, consider the new electric cars, which essentially are computers on wheels. Smartphones are really just small connected computers with an ever-growing list of sensors. Smart IoT devices like refrigerators and toasters are digitizing all manners of raw audio and video signals to enable touchless interfaces and to produce useful consumer analytics.
Third, the pandemic is also putting huge stress on the global semiconductor supply chains resulting in labor shortages for fabrication, testing, and assembly. Our reliance on tech devices to support remote working environments adds to the already stressed global demand.
How are businesses mitigating the crisis?
Gartner has warned that the shortage will persist until at least the second quarter of 2022, and given the uncertainty in the pandemic and global economics, the chip shortage crisis won’t be over anytime soon. Businesses are re-evaluating their supply chain, including diversifying the supplier base. For example, Intel just announced they will be producing chips for Qualcomm. This is a good example of risk mitigation with local/regional sourcing. Others are resorting to stockpiling chips to address both sourcing issues and possibly other geopolitical sanctions.
More innovative companies are exploring alternative solutions, including using substitute chips. There is more hard work involved, including rewriting software and firmware to support the alternative chips. Tesla has recently reported using this approach just to keep up with the production level.
How LatentAI Can Help Solve the Chip Shortage Crisis
Latent AI can help companies directly mitigate risk and revenue loss during the global chip shortage. With the Latent AI Efficient Inference Platform (LEIP) Software Development Kit (SDK), businesses have an alternative software-based solution to weather out the crisis.
The LEIP SDK consists of end-to-end developer tools that help AI practitioners extract the best performance of an AI model. LEIP is designed to take the hard work out of AI system development and deployment, by making it easy for AI scientists, software developers, and IT/OT professionals to solve real-world problems.
There are several ways in which LEIP help unlock hardware capabilities:
- Heterogeneous hardware targets
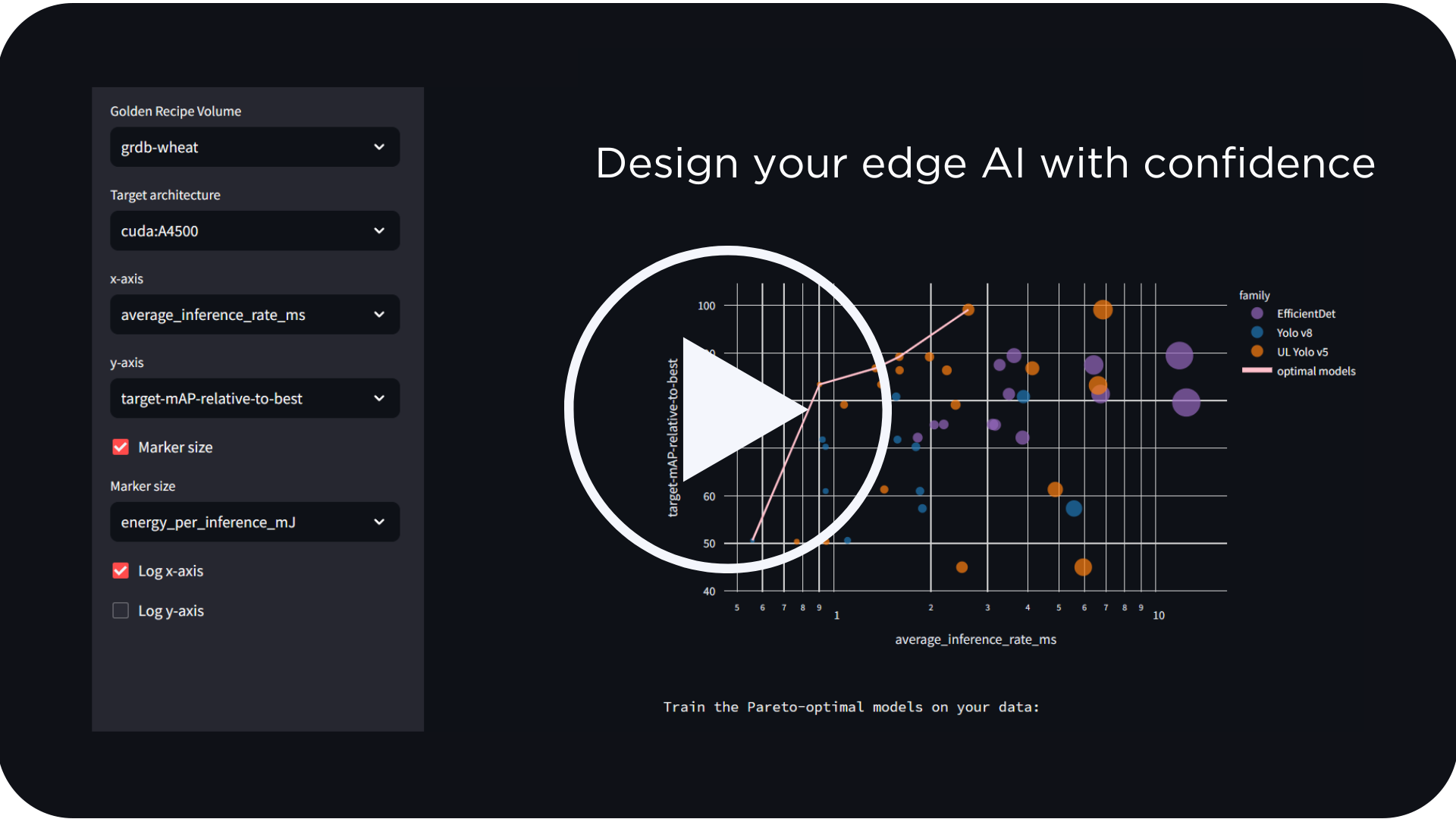
LEIP can optimize and target a wide variety of hardware including CPU, GPU, and DSP. We have demonstrated support for Intel x86, ARM processors/microcontrollers, and Nvidia CUDA GPUs. Businesses can explore the use of alternative chips without the extra efforts to re-tune their algorithms toward a specific hardware target.
- More processing headroom
LEIP compresses and optimizes AI models resulting in less processing time. That means there are opportunities to reduce the required number of chipsets because the memory and compute footprint are much smaller. A 10x reduction in memory storage could mean fewer memory chips, which is a critical benefit during a chip shortage crisis.
- Multiple models per device
LEIP runtime engine can support multiple models. For example, a 3x reduction in processing latency means you could run more AI models on the same hardware and shrink the bill of materials. Alternatively, targeting smaller processor hardware can do the same job.
Conclusion
Latent AI’s mission is to enable next-generation AI factories to build efficient AI models. Developers can use Latent AI’s software tools to design, explore and target a variety of model architectures and hardware. With support for different chips, LEIP opens up design alternatives using efficient software to unlock hardware capabilities. It is an integral tool to help the next-generation AI factory scale production goals amidst a chip shortage crisis.